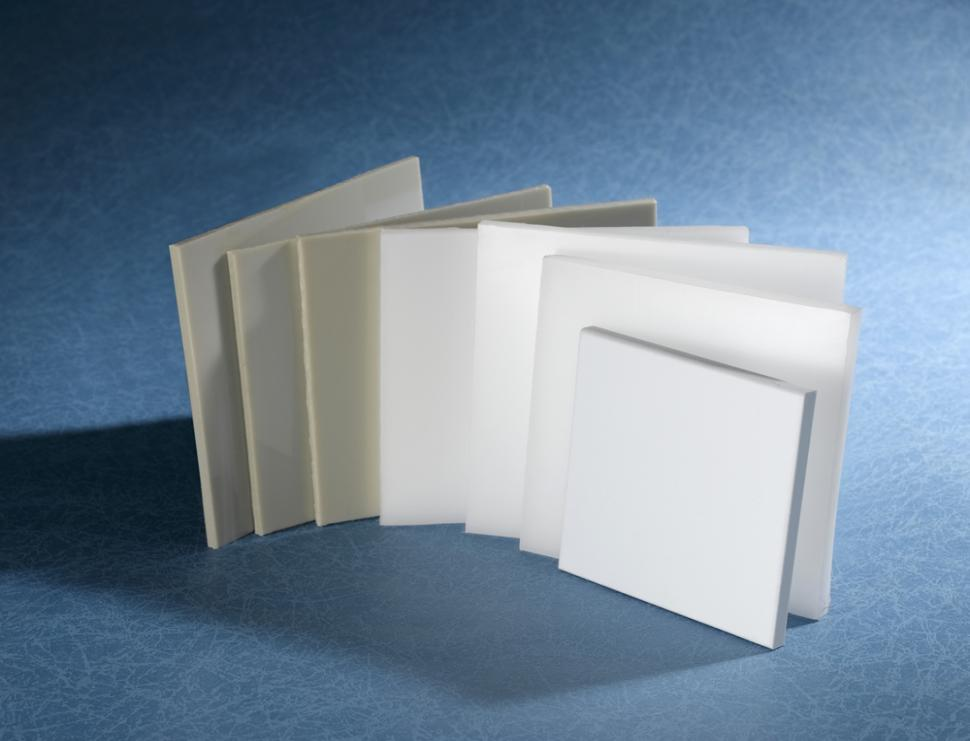
Polypropylene (PP) sheet has emerged as a game-changer in modern manufacturing, offering a compelling blend of durability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Derived from polypropylene resin, this lightweight yet robust material is redefining standards across sectors such as packaging, automotive, construction, and healthcare. Its unique properties—including chemical resistance, thermal stability, and ease of fabrication—position it as a frontrunner in meeting the evolving demands of industries worldwide.

One of the standout advantages of PP sheet lies in its exceptional mechanical performance. With a tensile strength ranging from 20 to 35 MPa and a flexural modulus of approximately 1,200–1,500 MPa, PP sheet can withstand heavy loads and repetitive stress without deformation. This resilience makes it ideal for applications requiring structural integrity, such as protective covers, automotive bumpers, and industrial components. Additionally, its low density (0.89–0.91 g/cm³) reduces weight while maintaining high rigidity, enhancing efficiency in transportation and construction projects.
Chemical resistance further solidifies PP’s versatility. It exhibits excellent inertness to acids, bases, solvents, and many organic chemicals, while maintaining stability in saltwater environments. This property ensures its suitability for applications in marine infrastructure, chemical processing plants, and food-grade equipment. For instance, PP sheets are commonly used in water pipelines and tank linings due to their ability to resist corrosion and maintain integrity over extended periods.
The material’s temperature adaptability spans from -20°C to +80°C, allowing it to function effectively in both cold climates and moderate heat environments. While continuous exposure to temperatures above 100°C may degrade its properties, short-term thermal resistance up to 120°C enables its use in transient high-heat scenarios. This balance between thermal resilience and cost-efficiency makes PP sheet a preferred choice over metal alternatives in budget-sensitive projects.
Another key benefit lies in its ease of fabrication. PP sheets are available in standard sizes and thicknesses, enabling precise cutting, welding, and thermoforming to meet specific design requirements. Their self-lubricating nature reduces maintenance needs, while the material’s compatibility with adhesives and coatings allows for enhanced surface customization. These attributes contribute to streamlined production processes and reduced operational downtime.
In conclusion, PP sheet’s blend of mechanical robustness, chemical inertness, and thermal adaptability renders it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing. Whether used for precision machinery components or large-scale infrastructure projects, its reliability and cost-efficiency continue to drive its adoption across industries. As engineering demands evolve, PP sheet remains a staple material poised to address future challenges through innovation and practicality.


